Synthesis and applications of double metal MXenes: A review
- 1 Department of Chemical Engineering, Arak Branch, Islamic Azad University, Arak, Iran
- 2 Chemical Engineering Faculty, Tarbiat Modares University, P.O. Box 14115-111, Tehran, Iran
- 3 Clean Energy Technologies Research Institute (CETRI), Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science, University of Regina, 3737 Wascana Parkway, Regina, SK S4S 0A2, Canada
- 4 School of Advanced Sciences, KLE Technological University, Hubballi 580031, India
- 5 King Abdullah Institute For Nanotechnology, King Saud University, Riyadh-11451, Saudi Arabia
- 6 Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), 1015 Lausanne, Switzerland
Abstract
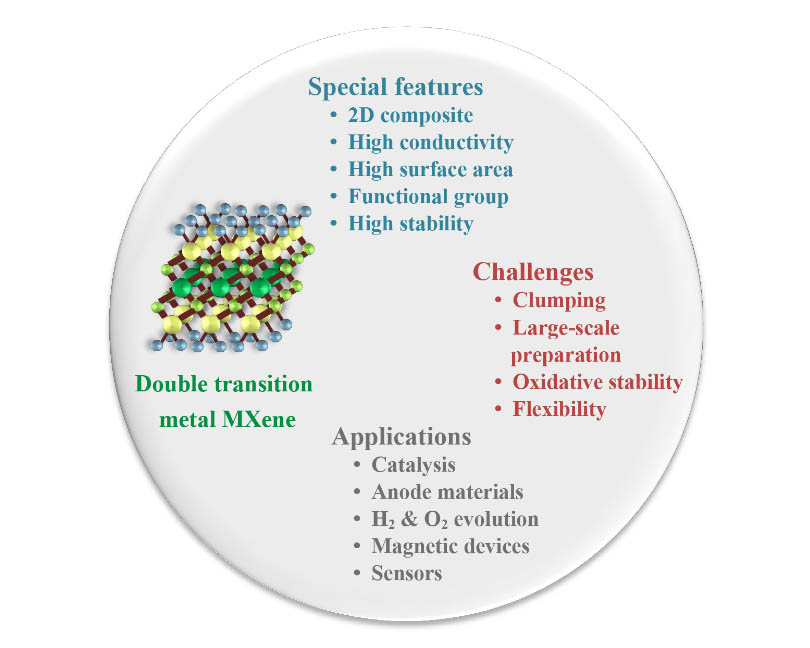
MXenes are known as a new type of two-dimensional layered materials that are composed of carbide, nitride, or carbonitride of transition metals. In the recent discovery of a new class of MXenes, two transition metals occupy the metal site, called double transition metal MXenes (DTM). These multilayer composites are of interest due to their attractive features such as high ion transport, extensive surface area, and biocompatibility. Some computational methods are used to predict the properties and performance of bimetallic carbonitrides. The most important feature of this category of materials is the stability and amount of formation energy, which directly affects the choice of material in various applications. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations are very beneficial to estimate the thermodynamic stability of DTM MXenes. Of course, proper surface modification with stable terminals is needed to overcome the limitations of DTM MXenes. In this review, the electrochemical, metallic, and magnetic properties of DTM MXene have been presented first. In the following, preparation methods are summarized according to the latest published findings. Then, various applications including hydrogen evolution reactions, anode materials in lithium and sodium batteries, nanomagnetic materials, and special applications have been investigated. Finally, more challenges, prospects, and suggestions for the development of two-dimensional DTM MXenes have been presented.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2023 Asieh Akhoondi, Mitra Ebrahimi Nejad, Mohammad Yusuf, Tejraj M. Aminabhavi, Khalid Mujasam Batoo, Sami Rtimi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












