Recent advances in hydrogen production using MXenes-based metal sulfide photocatalysts
- 1 Department of Chemical Engineering, Arak Branch, Islamic Azad University, Arak, Iran
- 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Mohaghegh Ardabili, P.O. Box 179, Ardabil, Iran
- 3 Department of Environmental Engineering and Science, Feng Chia University, Taichung 407, Taiwan
- 4 Department of Chemistry, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah 21589, P.O. Box 80203, Saudi Arabia
- 5 Department of Chemistry, School of Advanced Sciences, Vellore Institute of Technology (VIT), Vellore - 63014, India
Abstract
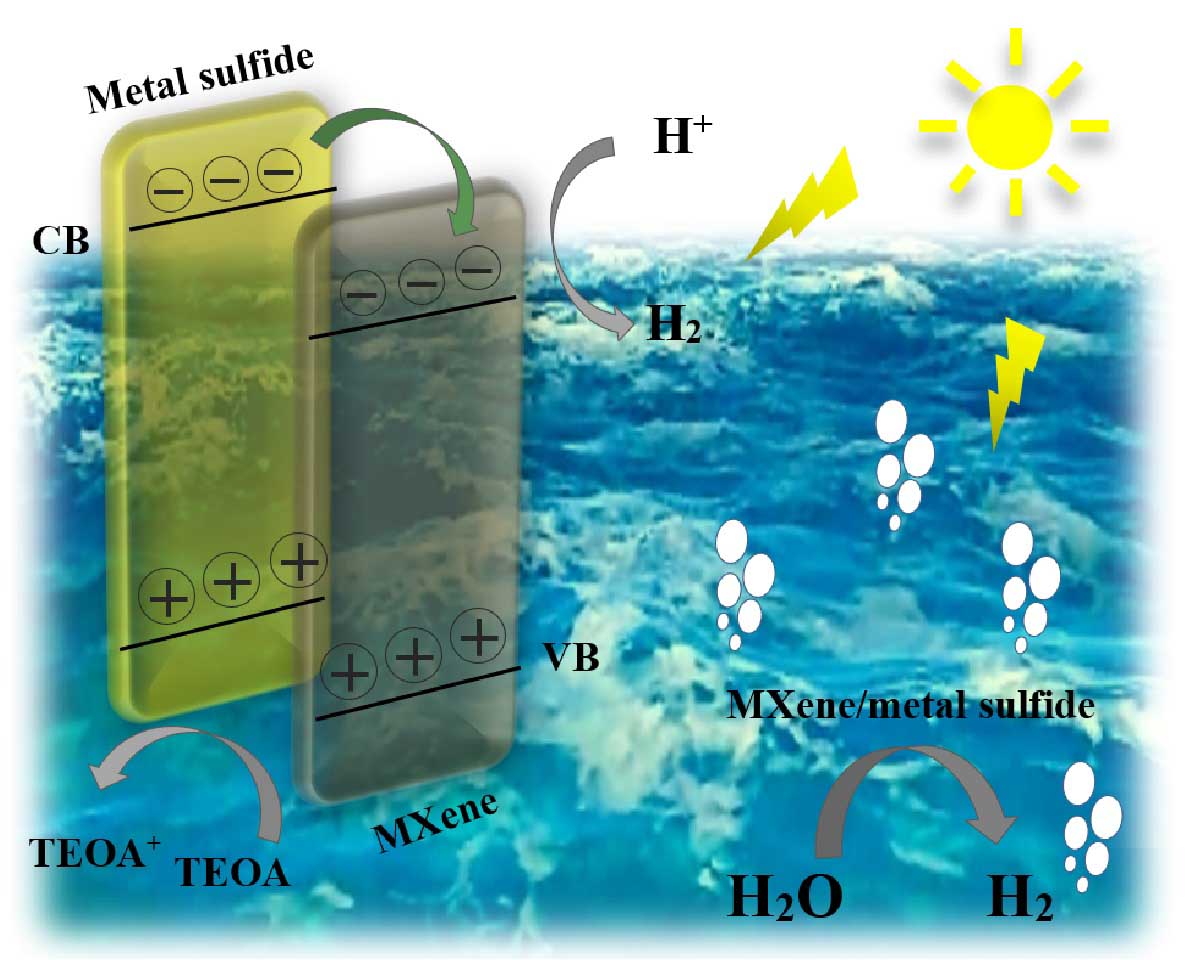
At present, the composition and crystalline structure of transition metal nitrides or carbides (MXenes) and their derivatives are continuously expanding due to their unique physicochemical properties, especially in the photocatalytic field. Advances over the past four years have led to improved preparation of new MAX phases, resulting in new MXenes with excellent photo-thermal effect, considerable specific surface area, long-term stability and optimum activity. Since MXenes have good electrical conductivity and their bandgap is adjustable under the visible light range, this group is one of the best promising candidates for hydrogen production from photo-splitting of water as an environment-friendly method of converting sunlight to chemical energy. Progress in noble metal-free photocatalyst associated with more understanding of the fundamental mechanism of photocatalysis has enabled a proper choice of cocatalyst with better efficiency. In this study, the photocatalytic production of hydrogen through MXens as a support and co-catalyst on metal sulfide is summarized and discussed. Recent advances in the design and synthesis of MXenes-based metal sulfide nanocomposites to increase the efficiency of photocatalytic hydrogen production are then highlighted. Finally, the challenges and future prospects for the development of MXenes-based metal sulfide composites are outlined.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2022 Asieh Akhoondi, Hadi Ghaebi, Lakshmanan Karuppasamy, Mohammed M. Rahman, Panneerselvam Sathishkumar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












