Effect of graphite die geometry on energy consumption during spark plasma sintering of zirconium diboride
- 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Mohaghegh Ardabili, Ardabil, Iran
- 2 Institute of Biomedical Engineering, University of New Brunswick, Fredericton, Canada
Abstract
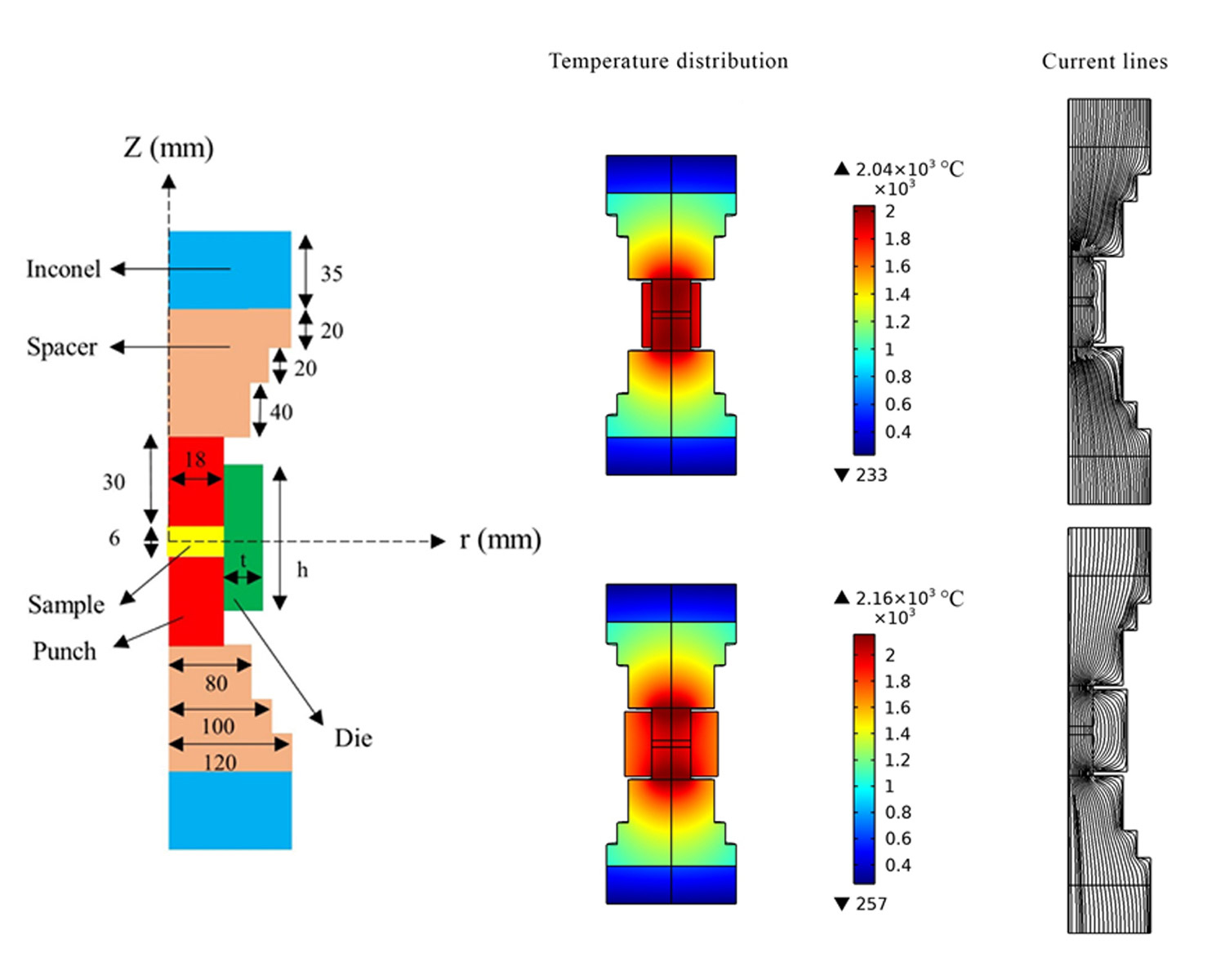
The present work aims to investigate the geometrical parameters of the graphite die on energy consumption needed for sintering of a ZrB2 sample. The Maxwell and electrical charge conservation equations are solved to obtain the electrical potential and current of the system. The governing equations are discretized by the Galerkin method and solved using the finite element method. The electric current distribution is obtained at each geometry and the temperature contours are obtained. The results showed that the height of die has a direct effect on power consumption. This can be attributed to the increased electric resistance and consequent increased Joule heating. On the other hand, increasing the die height resulted in more uniform temperature distribution through the sintered sample.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2021 Farhad Sadegh Moghanlou, Mohammad Vajdi, Milad Sakkaki, Shahla Azizi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












