Recent developments in chitosan-based adsorbents for tetracycline removal: A mini-review
- 1 Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Imam Hussein University, Tehran, Iran
- 2 Department of Mining and Geology, Qaemshahr Branch, Islamic Azad University, Qaemshahr, Iran
- 3 Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Basic Sciences, Shahrekord University, Shahrekord, Iran
- 4 Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Guilan, Rasht, 1841, Iran
Abstract
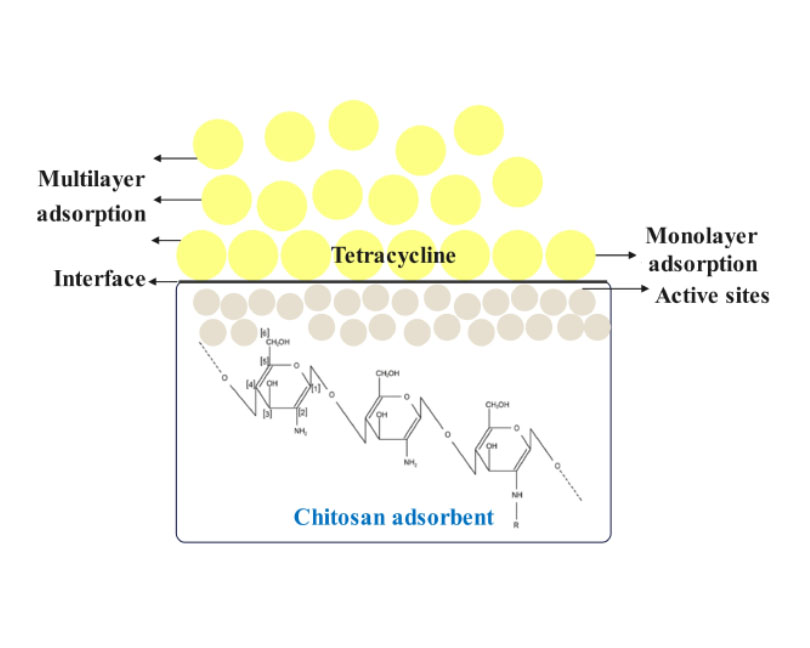
Tetracyclines (TCs) are widely used antibiotics that have raised concerns due to their presence in the environment, posing risks to human health and ecosystems. This mini-review explores recent advancements in utilizing chitosan-based adsorbents to remove TCs from wastewater efficiently. Our review reveals that adsorption performance is highly influenced by temperature and pH, with most studies reporting effective TC removal between 25–45 °C and pH values of 2–12. The Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models are both applicable, depending on the specific adsorbent, indicating both monolayer and heterogeneous adsorption behavior, with maximum adsorption capacities ranging from 19.32 mg/g to 940 mg/g, with the highest capacity shown for bacterial cellulose microfibers (BCM) char/chitosan (CS)/polyethyleneimine (PEI). Kinetic studies predominantly followed the pseudo-second-order model, suggesting chemisorption as a rate-limiting step, while some followed a pseudo-first-order model. High removal rates (≈ 90–99%) were reported for materials like zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-8)-chitosan, BCM char/CS/PEI, and carboxymethyl-chitosan (CMC)-modified Na-Mt (montmorillonite). This review highlights the significant potential of chitosan-based adsorbents. At the same time, further research is needed to optimize adsorption conditions, understand the mechanisms involved, and address the diverse sources of TC pollution. Given the global impact of TCs, a comprehensive approach encompassing enhanced monitoring, stricter regulations, the development of advanced treatment technologies like chitosan-based adsorbents, and public awareness campaigns is imperative to mitigate their environmental risks effectively.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2025 Alireza Pishevar, Milad Khanchoupan, Alireza Afradi, Fateme Kazemian, Gity Behbudi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












