Platinum-based electrochemical sensors for glucose detection: a mini-review
- 1 Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Imam Hussein University, Tehran, Iran
- 2 Department of Chemistry, Payame Noor University, East Tehran Branch, Tehran, Iran
- 3 Department of Exceptional Talents, Faculty of Medicine Sciences, Lorestan University of Medical Sciences , Khorramabad, Iran
- 4 Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Advanced Technologies, Quchan University of Technology, Quchan, Iran
Abstract
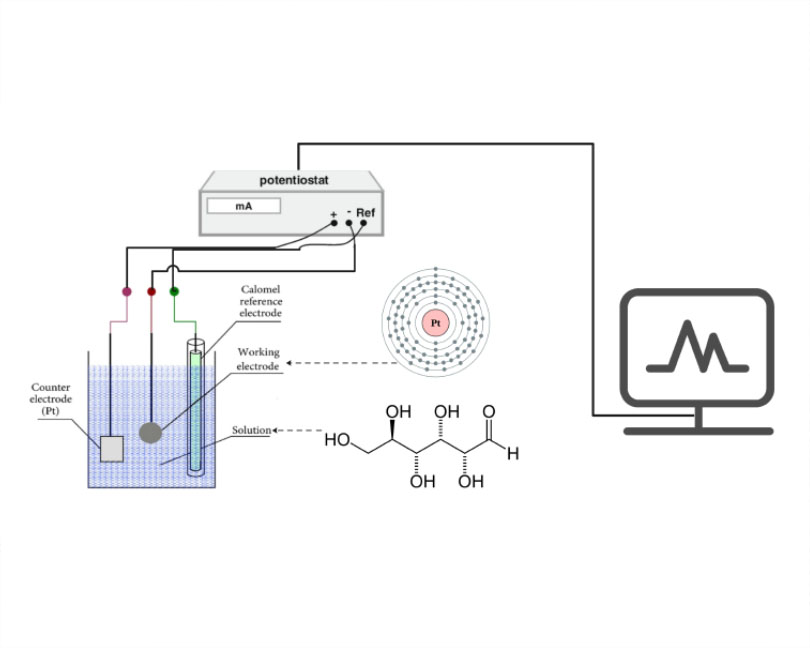
This mini-review provides a comprehensive overview of platinum-based electrochemical sensors for glucose detection, focusing on recent advancements in material design, fabrication techniques, and the application of single-atom catalysts. Platinum's exceptional electrocatalytic properties and inherent stability have made it a cornerstone material for developing sensitive, selective, and stable glucose sensors. Performance evaluations from the literature reveal sensors with sensitivities exceeding 850 μA/mM cm² and detection limits as low as 3.6 μM. This review examines various approaches to enhancing sensor performance, including the use of different platinum nanostructures (e.g., nanoparticles, nanowires), the incorporation of conductive polymers or metal oxides, and the application of various electrochemical techniques (e.g., amperometry, cyclic voltammetry). Despite these advancements, challenges remain in achieving improved selectivity, stability, and cost-effectiveness. Future research directions include exploring novel platinum-based materials, developing advanced fabrication techniques such as 3D printing, integrating microfluidic platforms, and leveraging single-atom catalysis to enhance sensor performance further. Developing reliable and efficient platinum-based electrochemical glucose sensors is crucial for advancing diabetes management, biomedical research, and point-of-care diagnostics. This review aims to inspire continued research and innovation in this promising field.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2024 Milad Khanchoupan, Alireza Pishevar, Donya Souri, Reza Yusofvand, Zeynab Dabirifar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












