Recent advances in synthesis, properties, and applications of nano-zero valent iron: A promising material for environmental remediation
- 1 Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Basic Sciences, Azarbaijan Shahid Madani University, Tabriz, Iran
- 2 Department of Chemistry, Payame Noor University, Tabriz, Iran
- 3 Department of Mining and Geology, Qaemshahr Branch, Islamic Azad University, Qaemshahr, Iran
- 4 Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology, Tehran, Iran
- 5 Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Guilan, Rasht, 1841, Iran
Abstract
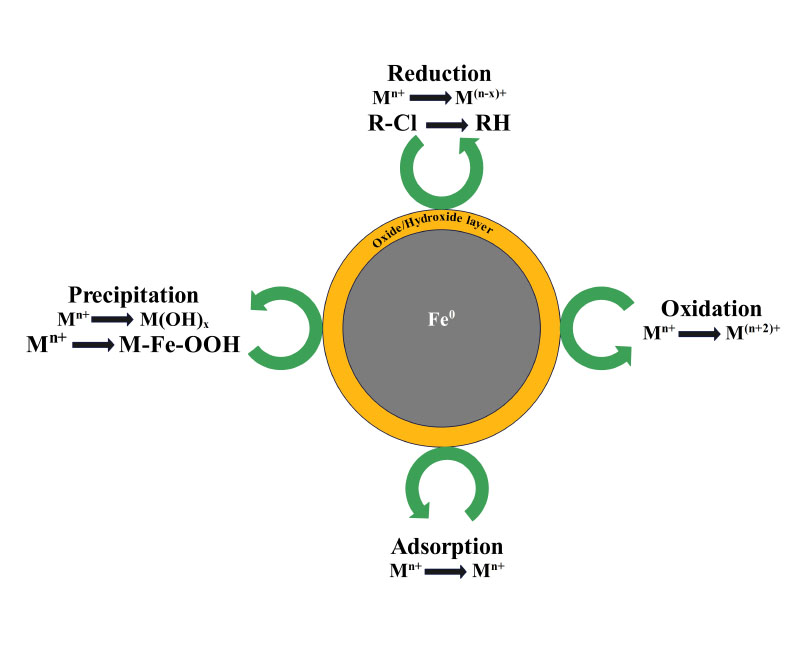
Nano-zero valent iron (nZVI) is increasingly recognized as a promising material for environmental remediation because of its high reactivity and efficient removal of various contaminants. This comprehensive review delves into the unique structure, synthesis techniques, and characterization methods of nZVI. It explores real-world applications of nZVI in remediating contaminated water, showcasing its efficacy in eliminating pollutants like heavy metals, organic compounds, and radionuclides. Studies suggest that nZVI composites demonstrate superior adsorption properties for heavy metals and pollutants with their distinctive core-shell structures and surface functional groups. Unlike conventional materials, nZVI composites exhibit heightened adsorption capabilities and easier retrieval from solutions, making them more effective in heavy metal removal. Moreover, the environmental ramifications of nZVI synthesis methods are critically analyzed, considering factors such as energy consumption and potential secondary pollution. The review underscores the significance of ongoing research and development to optimize nZVI's performance and reduce its environmental impact, thereby bolstering its role in promoting a sustainable environment.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2024 Mohammad Ghaffarzadeh, Reza Rasouli Khorjestan, Alireza Afradi, Aria Bandehpey, Gity Behbudi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












