Reactive spark plasma sintering of ZrB2-TiC composites: Role of nano-sized carbon black additive
- 1 Department of mechanical Engineering, University of Mohaghegh Ardabili, Ardabil, Iran
- 2 School of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology, 1684613114, Tehran, Iran
- 3 Department of Materials and Metallurgical Engineering, Amirkabir University of Technology (Tehran Polytechnic), Tehran, Iran
Abstract
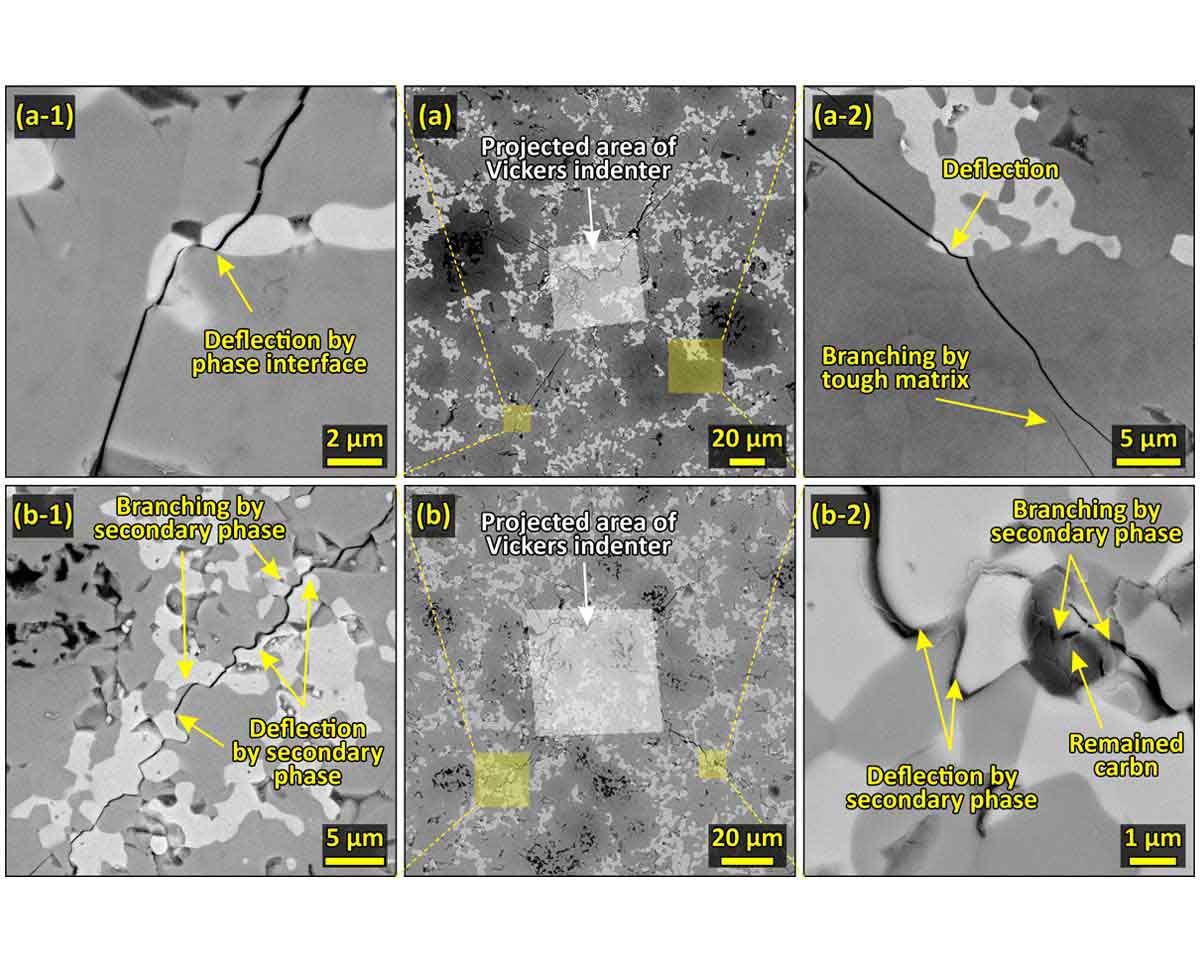
ZrB2-TiC composites with and without nano-sized carbon black as the sintering additive were densified through spark plasma sintering at 1900 °C for 7 minutes under the applied pressure of 40 MPa. The role of carbon black in densification behavior, phase arrangement, microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties of the sintered composites were then investigated. While both of the composite samples were found to be fully sintered, the thermodynamic of the reactive sintering was also studied. Results indicated that whereas the reactive sintering process leads to complete consumption of TiC through the formation of the solid solution as the matrix in both of the composite samples, the presence of carbon black at the initial composition of the samples can result in remained carbon at the final microstructure. Besides the in-situ synthesized zirconium carbide as the major reinforcement phase, such a remained carbon can lead to significantly different mechanical behavior of the composites. Accordingly, the hardness of 21.8 and 24.3 GPa and the indentation fracture toughness of 3.3 and 4.5 MPa.m0.5 were obtained for carbon-black free and doped samples, respectively. The densification, hardening, and toughening mechanisms in both of the composite samples were finally discussed.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2022 Hamid Istgaldi, Mehdi Mehrabian, Faramarz Kazemi, Behzad Nayebi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












