Corrosion and mechanical behavior evaluation of in-situ synthesized Cu-TiB2 nanocomposite
- 1 School of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering, Iran University of Science & Technology, Narmak, Tehran, Iran
- 2 Nano Science and Nano Engineering Department, Istanbul Technical University, Maslak, Istanbul, Turkey
- 3 College of Engineering, Thi-Qar University, Thi-Qar, Iraq
Abstract
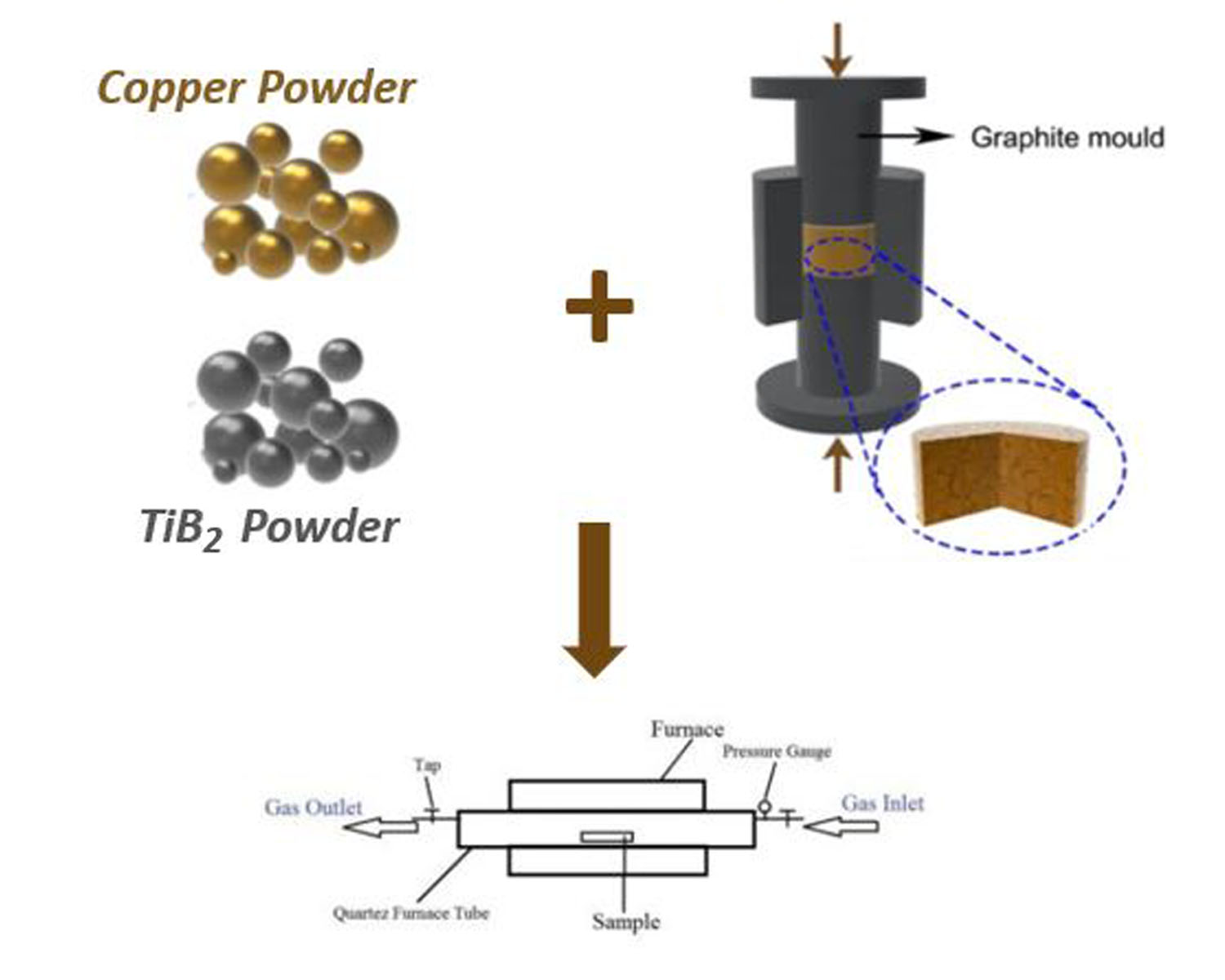
In this paper, the synthesis of the copper matrix nanocomposite and the effect of adding TiB2 nanoparticles on the copper matrix was investigated. Three different amounts of TiB2 nanoparticles 5, 10, and 15 wt% were added and sintering was carried out at 900 oC for 4 hours under argon atmosphere. The phase formation of achieved nanocomposites was studied by X-ray diffractometer and the morphology of the synthesized samples was studied by field emission scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy. The polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) at 3.5 wt% NaCl solution at room temperature was were carried out to evaluate the corrosion behavior of synthesized samples. Results show that adding the TiB2 nanoparticles decrease the corrosion resistance by the formation of galvanic couples, but the effect of amounts of porosities on the corrosion resistance is higher. It is revealed that the variation of the surface roughness is in direct relation to the value of polarization current density.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2021 Hossein Aghajani, Seyed Ali Naziri Mehrabani, Arvin Taghizadeh Tabrizi, Falih Hussein Saddam

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












