Beneficial effect of low BN additive on densification and mechanical properties of hot-pressed ZrB2–SiC composites
- 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Concordia University, Montreal, QC, H3G 1M8, Canada
- 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, York University, Toronto, ON, Canada
- 3 Saskpower Queen Elizabeth Power Station, 2211 Spadina Cres. W., Saskatoon, SK, S7M 5V5, Canada
Abstract
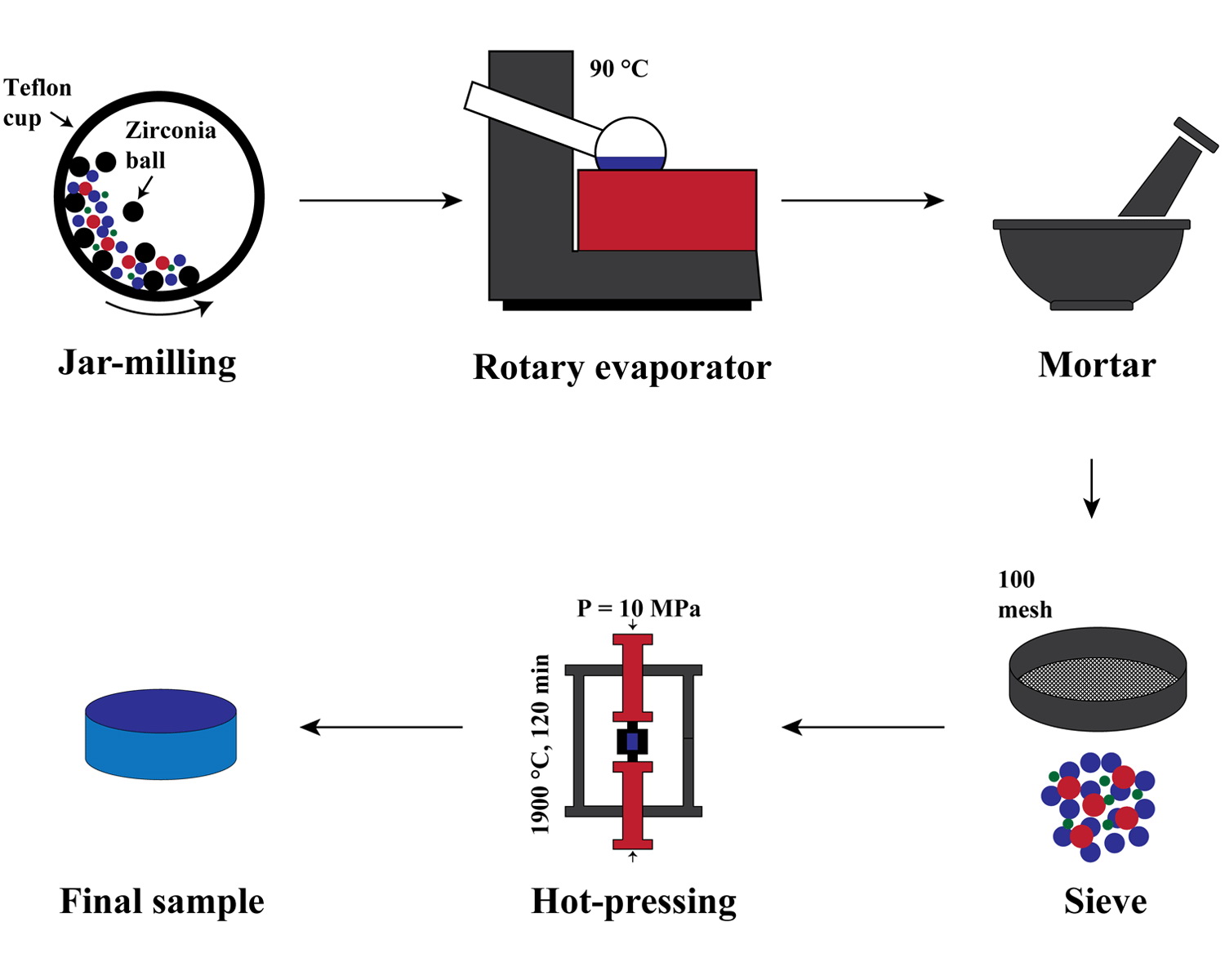
The incorporation of 1 wt% hexagonal BN (hBN) into ZrB2–30 vol% SiC could noticeably better the fracture toughness, hardness, and consolidation behavior of this composite. This research intended to scrutinize the effects of various amounts of hBN (0–5 wt%) on different characteristics of ZrB2–SiC materials. The hot-pressing method under 10 MPa at 1900 °C for 120 min was employed to sinter all designed specimens. Afterward, the as-sintered samples were characterized using X-ray diffractometry (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), and Vickers technique. The hBN addition up to 1 wt% improved relative density, leading to a near fully dense sample; however, the incorporation of 5 wt% of such an additive led to a composite containing more than 5% remaining porosity. The highest Vickers hardness of 23.8 GPa and fracture toughness of 5.7 MPa.m1/2 were secured for the sample introduced by only 1 wt% hBN. Ultimately, breaking large SiC grains, crack bridging, crack deflection, crack branching, and crack arresting were introduced as the chief toughening mechanisms in the ZrB2–SiC–hBN system.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2021 Saber Haghgooye Shafagh, Shapour Jafargholinejad, Siyamak Javadian

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












