Comparing the effects of different sintering aids on spark plasma sintering of SiC ceramics
- 1 Ceramics Department, Materials and Energy Research Center (MERC), P.O. Box 31779-83634, Karaj, Iran
Abstract
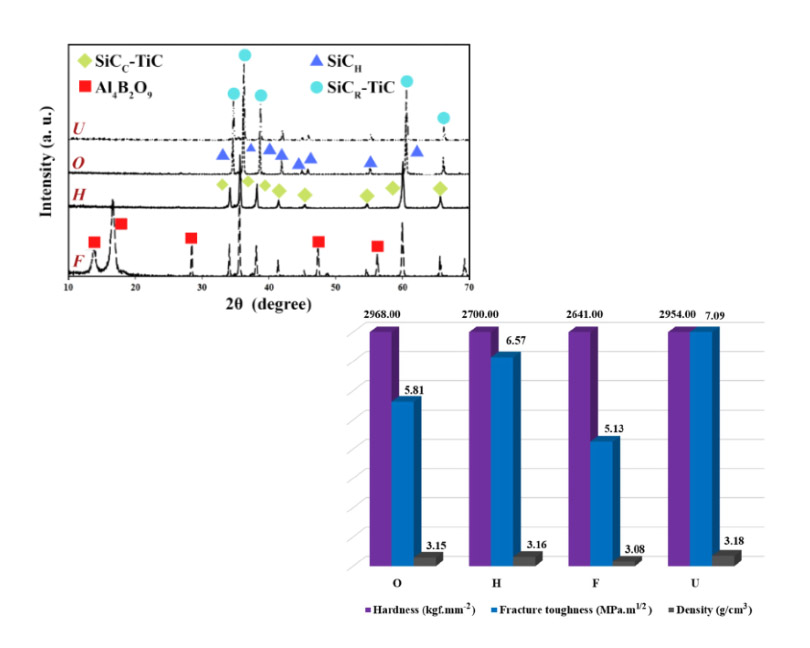
In the present work, to improve the mechanical properties of silicon carbide different sintering aids were used. 2.5 wt% B4C, 2.5 wt% AlN, and TiC in the range of 5 to 7 wt% were selected to manufacture the SiC-based sample via spark plasma sintering at 1700 °C. The results show that the use of 2.5 wt% B4C-2.5 wt% AlN additives increases the strength (1206 MPa) of the composite through the compressive stress created in the grain boundaries and decreases its fracture toughness (5.13 MPa.m1/2). But in the case of TiC-doped SiC, the toughness (7.09 MPa.m1/2) and density (3.18 g/cm3) of the sample increases compared to the pure SiC sample.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2024 A. Faeghinia

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












