Synthesis of magnetite-silica-carbon quantum dot nanocomposites for melatonin drug delivery
- 1 Ceramics Department, Materials and Energy Research Center (MERC), P.O. Box 31779-83634, Karaj, Iran
Abstract
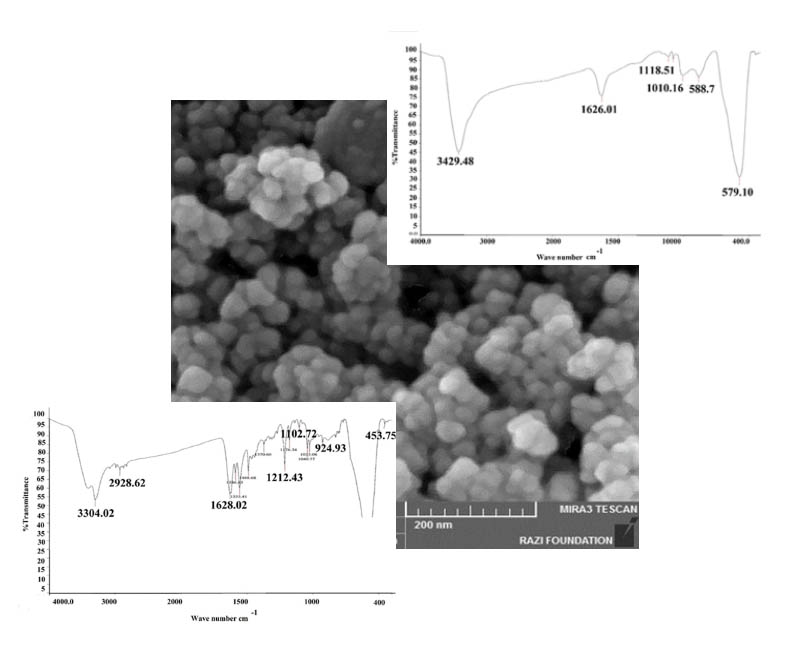
In targeted drug delivery, the drug is released at a specific and desired point and condition. In this research, magnetite cores (high saturation magnetization property (emu.g-159) were used to target the drug system. First, magnetite nanoparticles were synthesized by coprecipitation method from divalent and trivalent chloride salts of iron (FeCl2 and FeCl3), then mesoporous silicas (with a pore diameter of 13 nm) were formed by Stöber's method from the tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) silica source on magnetite cores in spheres form. After that, the carbon quantum dots were synthesized by hydrothermal method from citric acid and their surface was immobilized by dimethylamine which were placed in silica cavities by physical adsorption method.
The effective drug melatonin (6.46 mg of melatonin per 100 mg of the drug system) was also loaded on this system by physical absorption method and the release of this drug was carefully determined by the release from the dialysis bag in the simulated environment of blood and cancer tissue. the quantum gain of the system was determined to be about 40%. The results showed that the loading of melatonin drug and carbon quantum dots was done well on silica nanoparticles with magnetite cores, and this system releases 30% of the drug even under temperature conditions.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2023 A. Faeghinia, Hossein Nuranian, Mojtaba Eslami

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












