Sol-gel zinc oxide nanoparticles: advances in synthesis and applications
- 1 Catalyst and Nano Material Research Laboratory (CNMRL), School of Chemical, Petroleum and Gas Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology, Tehran, Iran
- 2 Advanced Materials Research Center, Department of Materials Engineering, Najafabad Branch, Islamic Azad University, Najafabad, Iran
- 3 Department of Mining and Metallurgy, Yazd University, Yazd, Iran
- 4 Semiconductor Department, Materials and Energy Research Center, Karaj, Iran
- 5 Department of Materials Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran
Abstract
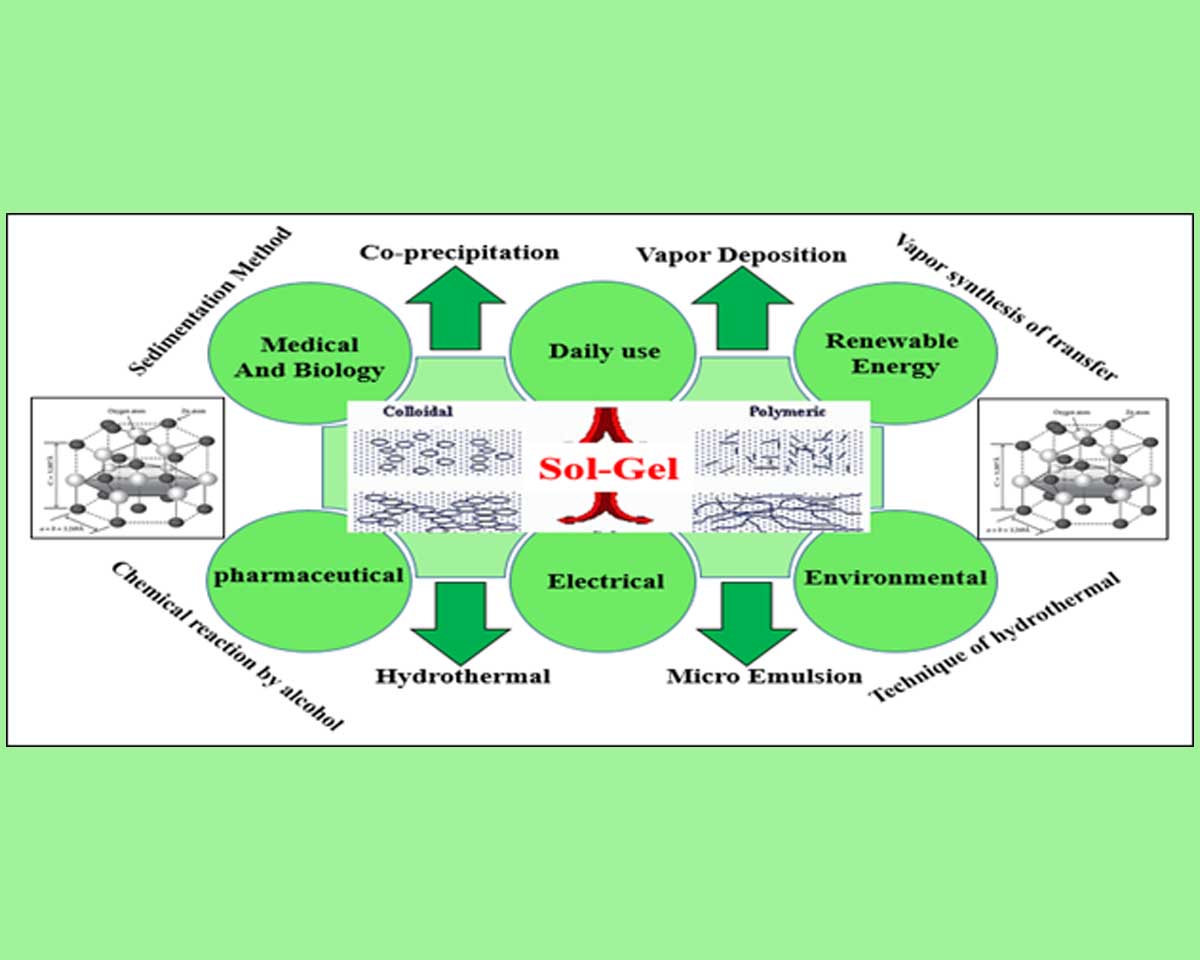
Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO) exhibit numerous characteristics such as biocompatibility, UV protection, antibacterial activity, high thermal conductivity, binding energy, and high refractive index that make them ideal candidates to be applied in a variety of products like solar cells, rubber, cosmetics, as well as medical and pharmaceutical products. Different strategies for ZnO nanoparticles’ preparation have been applied: sol-gel method, co-precipitation method, etc. The sol-gel method is an economic and efficient chemical technique for nanoparticle (NPs) generation that has the ability to adjust the structural and optical features of the NPs. Nanostructures are generated from an aqueous solution including metallic precursors, chemicals for modifying pH using either a gel or a sol as a yield. Among the various approaches, the sol-gel technique was revealed to be one of the desirable techniques for the synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles. In this review, we explain some novel investigations about the synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles via sol-gel technique and applications of sol-gel zinc oxide nanoparticles. Furthermore, we study recent sol-gel ZnO nanoparticles, their significant characteristics, and their applications in biomedical applications, antimicrobial packaging, drug delivery, semiconductors, biosensors, catalysts, photoelectron devices, and textiles.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2021 Parisa Shafiee, Mehdi Reisi Nafchi, Sara Eskandarinezhad, Shirin Mahmoudi, Elahe Ahmadi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












