Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti3SiC2 MAX phases sintered by hot pressing
- 1 Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Tabriz, Tabriz, Iran
Abstract
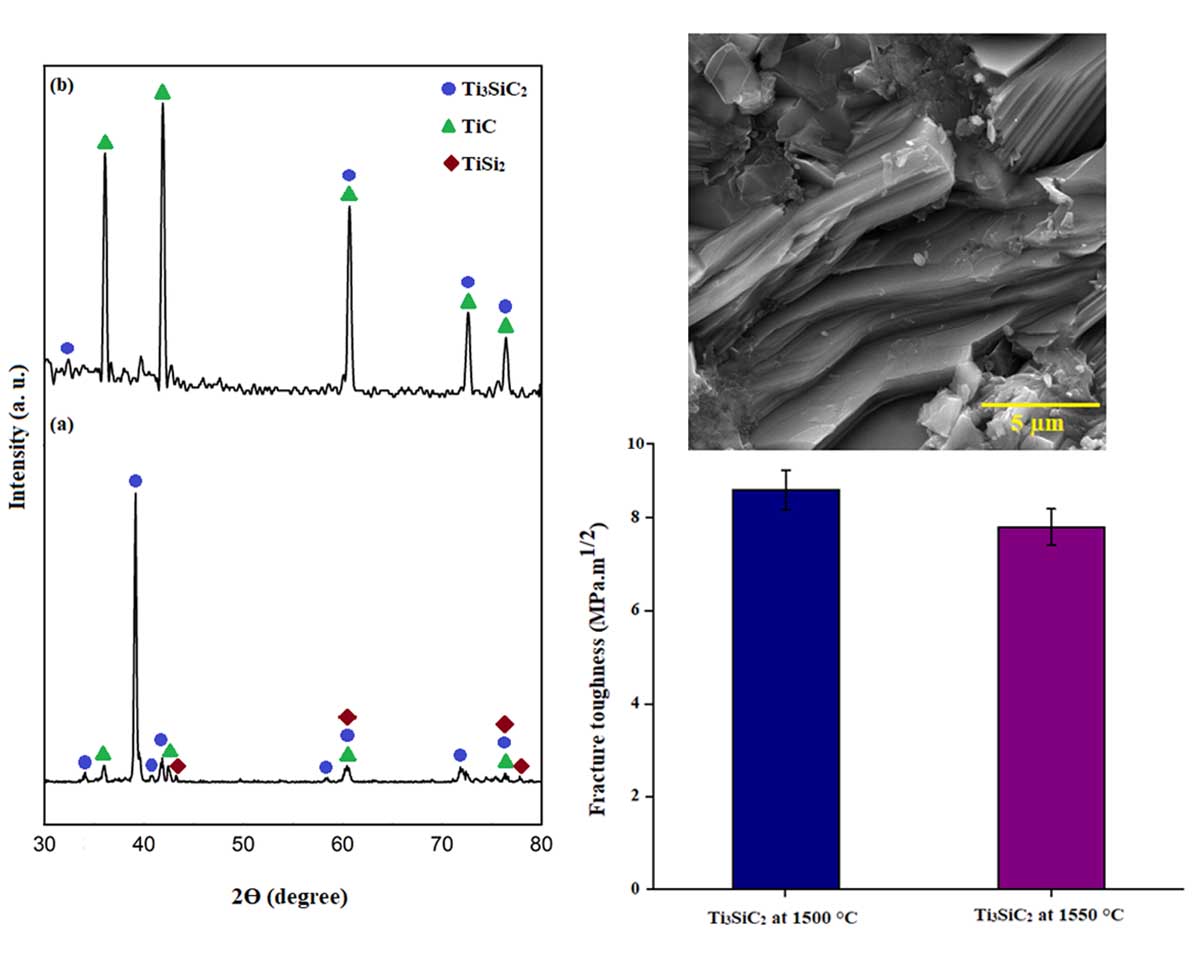
This study aimed to investigate the effect of sintering temperature on Ti3SiC2 samples' microstructure and mechanical properties, including three-point flexural strength, Vickers hardness, and fracture toughness. Therefore, Ti3SiC2 samples were sintered under a vacuum atmosphere at a pressure of 35 MPa for 30 minutes at two temperatures of 1500 and 1550 °C by hot pressing. The microstructure obtained from the fracture cross-section of the samples shows that by increasing the sintering temperature to 1550 °C the microstructure of this sample becomes larger than the sintered sample at 1500 °C. Also, increasing the sintering temperature to 1550 °C causes the decomposition of Ti3SiC2 to TiC, which can be seen in the X-ray diffraction pattern (XRD). In addition, the relative density of the sintered sample at 1550 °C is 98.08% which is higher than that of the sintered sample at 1500 °C with the result of 89%. On the other hand, the three-point flexural strength (227.5 MPa), the Vickers hardness (~9 GPa), and the fracture toughness (8.6 MPa.m1/2) of the sintered sample at 1500 °C are higher due to the fine-grained structure.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2021 Sheida Haji Amiri, Nasser Pourmohammadie Vafa

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












