Sintering behavior and microwave dielectric properties of CaTi1-x(Nb1/2Al1/2)xO3
- 1 Laboratory of Functional Materials and Devices, Department of Physics, Abdul Wali Khan University Mardan, 23200 KP, Pakistan
Abstract
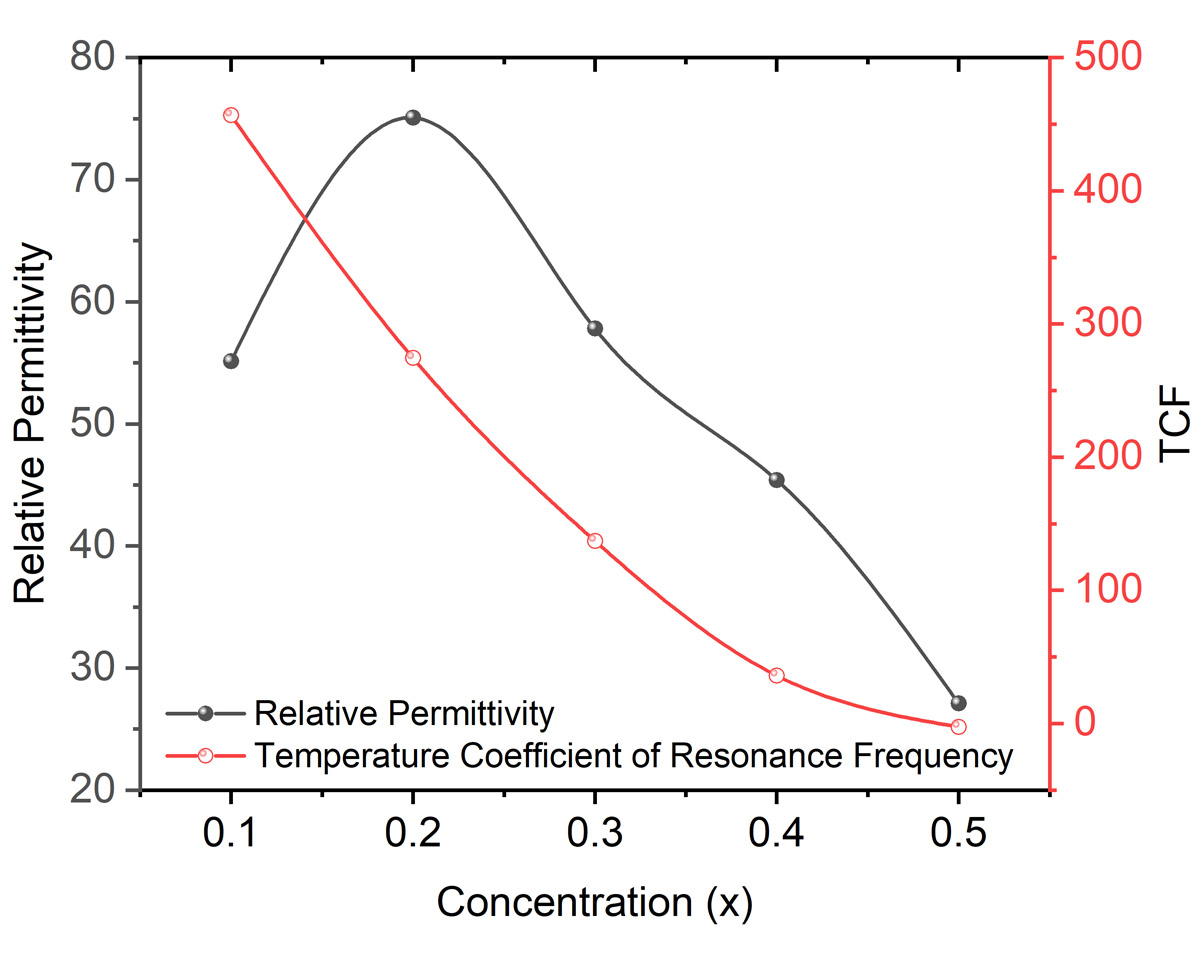
CaTi1-x(Nb1/2Al1/2)xO3 with x=0.1–0.5 ceramics were processed through solid state sintering. X-rays diffraction (XRD) patterns of the compositions showed that the samples have orthorhombic crystal structure with symmetry (Pbnm). The symmetry was further confirmed using Raman spectroscopy. A total of 13 Raman modes were detected, which were in agreement with the XRD results. Microstructure analysis of the samples showed porosity in the samples, presumably due to the substitution of Al, having high melting point. As the concentration of Al and Nb increased, relative permittivity (er), quality factor (Q×fo) and temperature coefficient of resonance frequency decreased. Optimum microwave dielectric properties were achieved for the composition x=0.5 sintered at 1650 °C for 8 h i.e., er ~27.09, Q×fo ~17378 GHz, and tf ~ -2.5 ppm/°C.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2021 Akbar Khan, Asif Ali, Izaz Khan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












