The effect of synthesized Cu2O on the microbial corrosion inhibition of urban sewer systems
- 1 Department of Chemical Engineering, Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran
- 2 Department of Chemical Engineering, Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, Kerman, Iran
- 3 Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, the University of Texas at Arlington, USA
Abstract
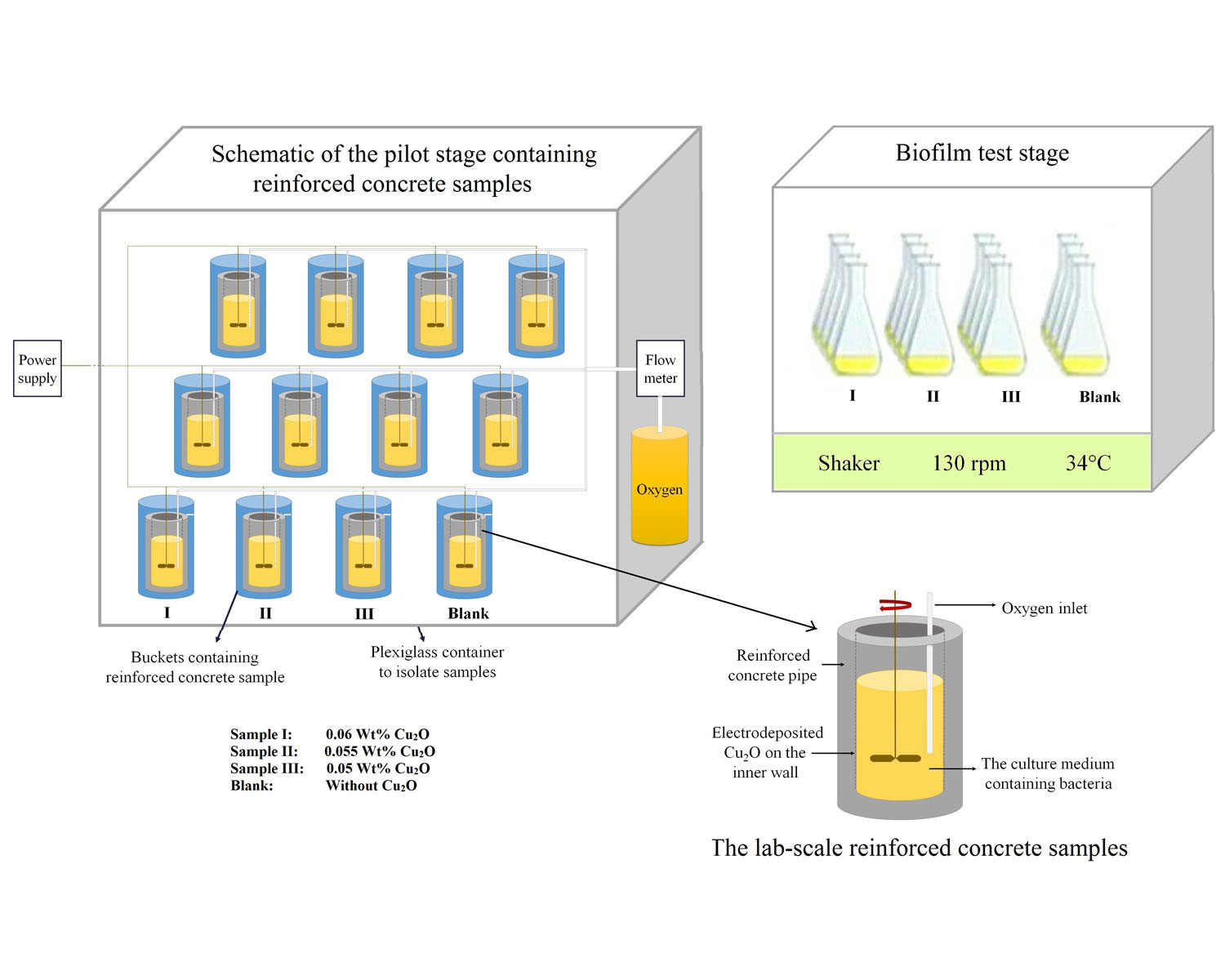
The microbial corrosion of reinforced concrete sewers was inhibited by synthesized cuprous oxide (Cu2O) nanoparticles. The antibacterial characteristics of Cu2O on Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans were investigated by temporal variation of pH, turbidity, and bacterial counting. Three reinforced concrete samples with different weight percentages of electrodeposited Cu2O (0.06 wt%, 0.055 wt %, 0.05 wt %) were used. The bacterial counting showed that the number of bacteria in samples with 0.06, 0.055, and 0.05 wt% of Cu2O was 4.82, 4.42, and 2.94 times lower than the blank sample (BS), respectively. After bacterial growth, the optical density measurement showed that the percentage of turbidity enhancement for samples with 0.06, 0.055, and 0.05 wt% of Cu2O were 108%, 118%, 165%, respectively, while it was 412% for the BS. Moreover, the pilot stage's pH monitoring revealed that the electrodeposited Cu2O lowered the concentration of hydronium between 7 to 81 times compared to the BS. Experiments indicated that slight changes in the amount of electrodeposited Cu2O lead to significant changes in samples' ability to hinder bacterial growth and microbial-induced corrosion.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2021 Zahra Khademmodaresi, Fereshteh Bakhtiari, Mohammadmehdi Azizi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












