High-temperature spark plasma sintering of h-BN composites reinforced with carbon nanotubes, carbon fibers, and graphene nanoplates
- 1 Faculty of Materials and Manufacturing Technologies, Malek Ashtar University of Technology, Tehran, 1491912354, Iran
- 2 Non-Metallic Materials Research Group, Niroo Research Institute (NRI), Tehran, 14686-13113, Iran
Abstract
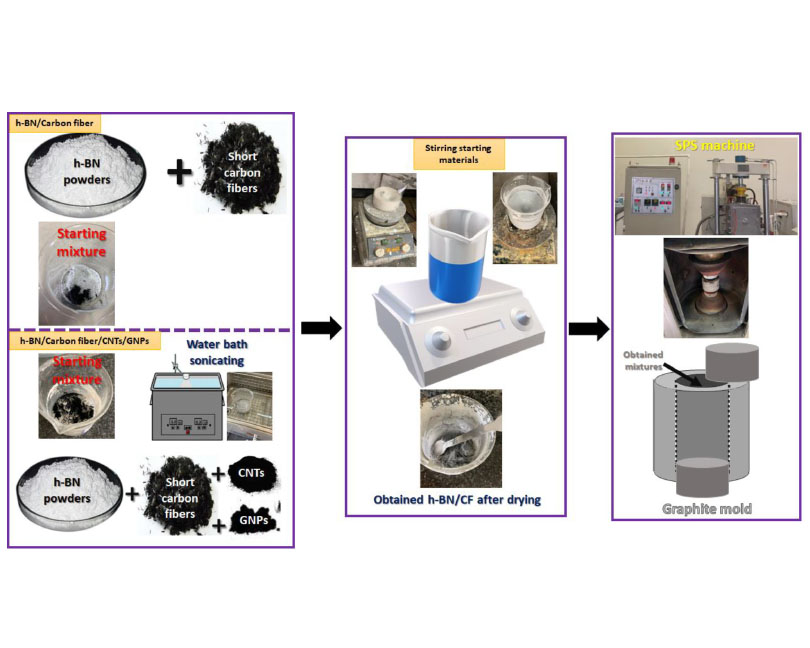
In this study, two h-BN-based composites reinforced with carbon fibers (CF) and carbon fibers/carbon nanotubes (CNTs)/graphene nanoplates (GNPs) have been produced successfully through a high-temperature spark plasma sintering. 1 wt% short carbon fibers (length of 5 mm) with 0.1 wt% of CNTs and also 0.1 wt% of GNPs as hybrid composite were mixed through a simple mixing method including a high energy sonicating and stirring on the hot plate in ethanol media until drying. Moreover, the h-BN/1 wt% CF composite was mixed with a similar method to compare the impacts of CNTs and GNPs addition on the mechanical properties and microstructure of the h-BN/CF composite. The high-temperature spark plasma sintering processes were performed at vacuum conditions of almost 20–25 MPa with a starting pressure of 10 and a final applied pressure of 50 MPa at a maximum temperature of 1900 °C. Both prepared samples showed near full densification of higher than 98.1% of the theoretical density determined by Archimedes’ principle. Investigation of the crystalline phases by XRD represented only related peaks to h-BN. The FESEM images indicated an almost uniform distribution of reinforcement in the h-BN matrix. Furthermore, the polished surface of the provided samples showed only the pulled-out carbon fibers effects while the fracture surfaces confirmed the presence of CF and its tunneling effects. The obtained mechanical properties revealed 273±12 MPa of bending strength, 1.32±0.1 GPa of Vickers hardness, and 4.79±0.2 MPa.m0.5 fracture toughness for the prepared hybrid composite.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2024 Hossein Eslami-Shahed, Khanali Nekouee, Farhad Moravvej-Farshi, Fatemeh Dabir

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












