Neutron shielding performance of polyethylene-7% B and Al-30 wt% B4C composites fabricated via hot-press sintering
- 1 Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Bonab, P.O. Box 5551761167, Bonab, Iran
- 2 Reactor and Nuclear Safety Research School, Nuclear Science and Technology Research Institute (NSTRI), Tehran, Iran
- 3 Nuclear Fuel Cycle Research School, Nuclear Science and Technology Research Institute (NSTRI), Tehran, Iran
Abstract
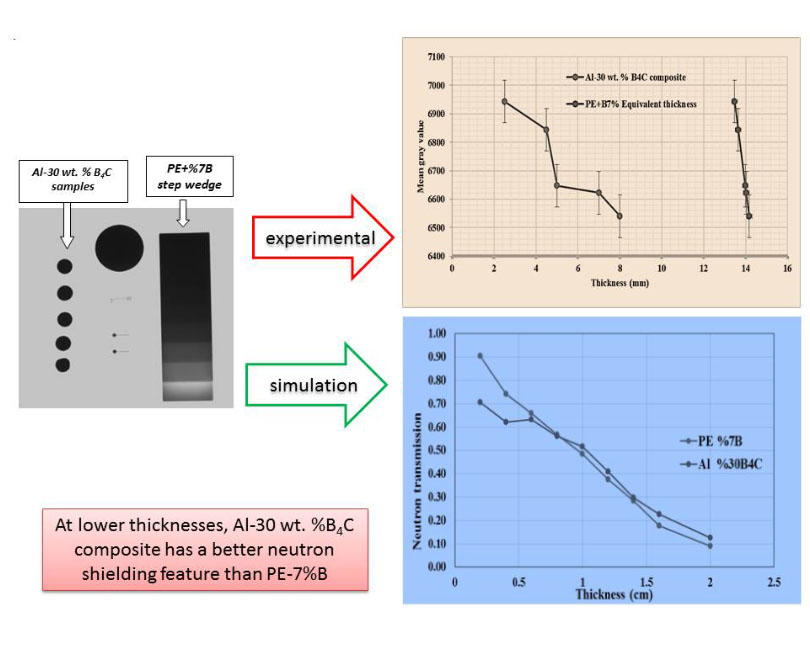
The current research investigates the neutron shielding features of polyethylene-7% B and Al-30 wt% B4C composites fabricated via hot-press sintering. The practical analysis was conducted via Neutron radiography and Monte Carlo N-Particle (MCNP) simulation. The results illustrated that Al-30 wt% B4C with 5 mm thickness has equivalent neutron absorption properties with 14 mm thickness of PE-7% B. Composites with higher density and homogenous distribution of B4C have better neutron shield properties. Al-30 wt% B4C composite fabricated at 650 °C has a higher neutron absorption property. Experimental and simulation findings confirmed each other at lower thicknesses and Al-30 wt% B4C has better neutron shielding than PE-7% B. At thicknesses over 1 cm, the cross-sectional area of polyethylene-7% B and Al-30 wt% B4C composites are near each other. By increasing the thicknesses of composites, the relative total dose reduction and the shield properties of composites are enhanced.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2024 Masomeh Ghayebloo, Zeinab Naghsh Nejad, Nafiseh Araghian, Hamzeh Foratirad, Amir Movafeghi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












