Enhanced methyl green adsorption of ZIF-8 metal-organic framework: Insights from different solvents
- 1 Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Mohaghegh Ardabili, Ardabil 5619911367, Iran
Abstract
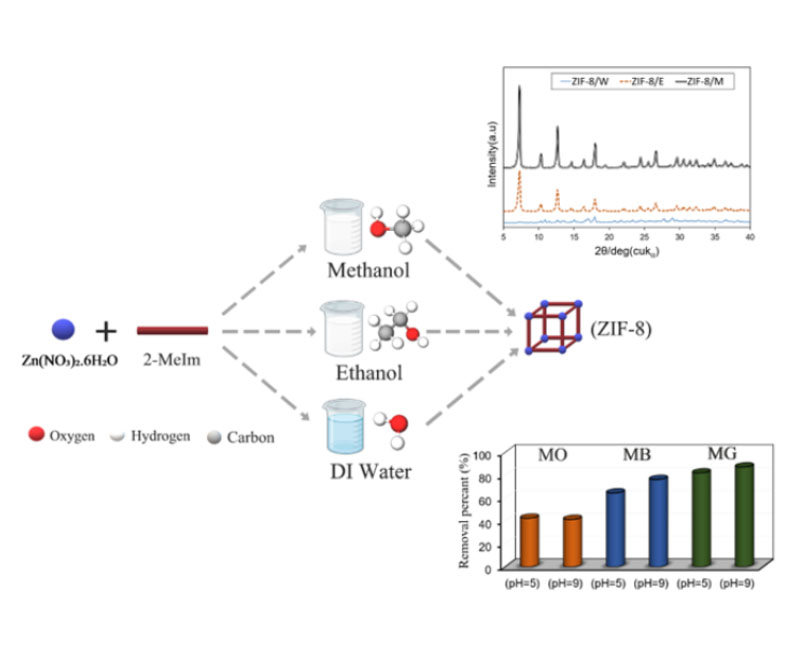
This study investigates the effect of solvent type on the structural properties and adsorption performance of the ZIF-8 metal-organic framework for removing various dyes including, methyl green (MG), methylene blue (MB), and methyl orange (MO) from water in acidic and alkaline environments. ZIF-8 samples were synthesized using zinc nitrate, methylimidazole, and three different solvents including, water, methanol, and ethanol under atmospheric pressure and 70 °C. Characterization using BET, XRD, FT-IR, and TGA techniques sheds light on the structural, chemical, and thermal properties of ZIF-8 samples. Among the samples, ZIF-8/M, synthesized using methanol, stands out, demonstrating the high surface area of 2172.7 m2/g, large total pore volume of 1.5412 cm3/g, and high crystallinity of 31.9% with improved thermal stability. Furthermore, ZIF-8/M shows better adsorption performance for methyl green with a removal percentage of 81.9%, 87.1%, and an adsorption capacity of 20.5 mg/g and 21.8 mg/g, in acidic and alkaline environments, respectively. Enhanced dye adsorption of ZIF-8/M is associated with both physical and effective chemical adsorption mechanisms via tuning the environment's acidity.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2024 Saeid Zahedi Asl, Fahimeh Hooriabad Saboor

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












