Comsol Multiphysics modeling of an electrochemical biosensor using carbon nanotubes for detecting urinary estrogen receptor
- 1 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Eastern Mediterranean University, Famagusta, via Mersin 10, Türkiye
Abstract
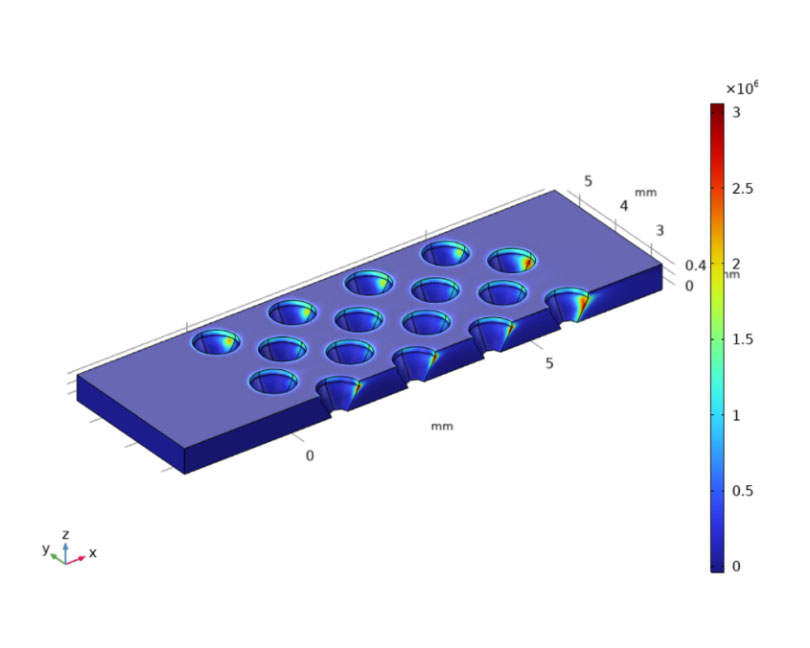
A class of steroid hormones known as estrogens is essential for the health of the heart, bones, and reproductive system. Changes in estrogen levels have been connected to several health problems, such as endocrine disorders, metabolic syndromes, and cancer. In pharmaceutical applications, environmental monitoring, and medical diagnostics, biosensors that measure estrogen levels are essential. This study models estrogen detection biosensors based on urine liquid, horseradish peroxidase biorecognition, and carbon nanotubes (CNT) using Comsol Multiphysics. This study demonstrates that most interactions happen at the upper boundary of the concave pillars put inside the box. Besides, it shows that the velocity has the highest value between the concave pillars inside the box. The results demonstrate that the number of interactions (absorption and adsorption) rises with increasing the concave pillars' area, affecting the biosensor output.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2024 Lenah Serai Wangare, Thamsanqa Mafika, Muneebah Ally Said El-Kitany, Shahla Azizi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












