Synthesis of molybdenum carbide using mechanochemical and thermal approaches
- 1 Department of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering, Hamedan University of Technology, Hamedan, 65155-579, Iran
Abstract
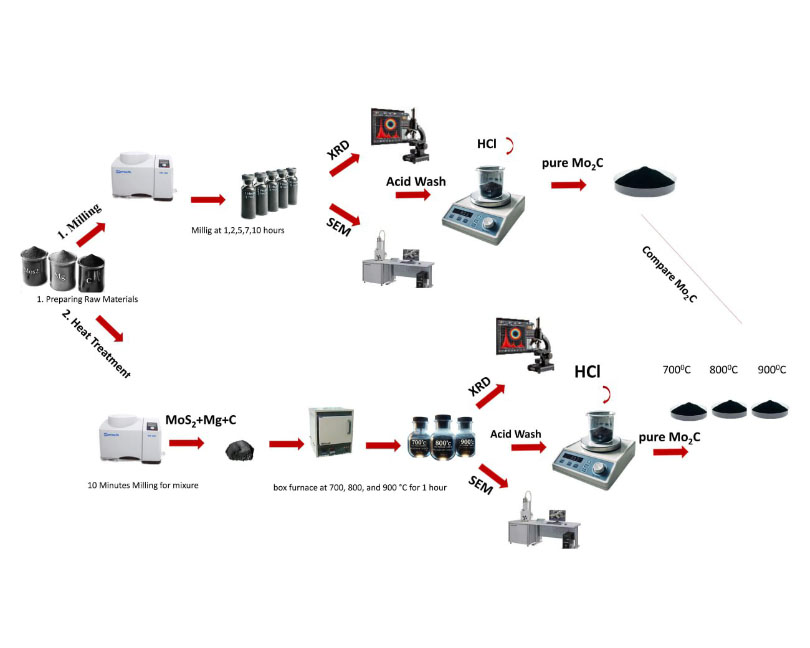
The carbothermic reduction of MoS2 using Mg, an efficient sulfur scavenger, was carried out by two very different routes, i.e., mechanochemical reaction and heat treatment. The thermodynamic calculation results show that Mo2C and MgS are the phases formed when the elements are combined, and carbothermic reduction of molybdenite takes place. XRD analysis data indicates no reaction occurred at 1, 2, and 5 h of milling by the mechanochemical method, and the initial phases MoS2, Mg, and C were identified. On the other hand, after 7 hours of milling, Mo2C and MgS phases finally emerged. Through heat treatment, the desired Mo2C and MgS phases were successfully prepared with the crystal diffraction spots obvious at 700, 800, and 900 °C, respectively. Both of these methods produced powders which were then washed with a 10% 1M HCl solution, and as a result, a reasonable yield of pure molybdenum carbide was obtained.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2024 Pegah Mohazab, Samad Ghasemi, Akbar Heidarpour

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












