Effect of chemical composition on fabrication of HAp-YSZ-Ti composites by spark plasma sintering method
- 1 Ceramics Department, Materials and Energy Research Center (MERC), Karaj, Iran
Abstract
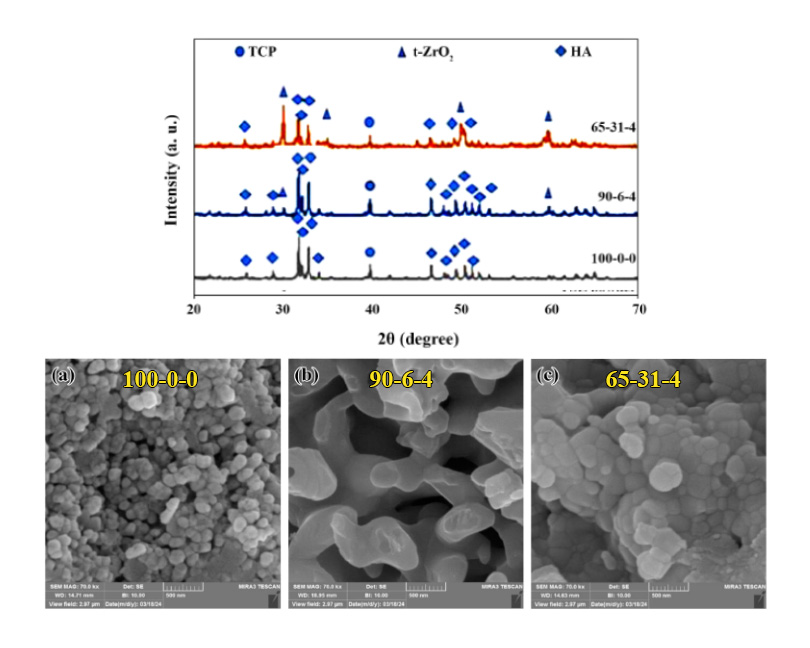
This research examines the thermal behavior and sintering characteristics of hydroxyapatite (HAp) composites with yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) and titanium using the spark plasma sintering (SPS) method. This study uses simultaneous thermal analysis (STA) to investigate the decomposition behavior of composites. During the sintering process, data on displacement, temperature, time, and current were recorded. A key challenge encountered was the fracture and crushing of the samples after the sintering process. The results show that the decomposition temperature of pure HAp (sample 100-0-0) occurs around 800 °C. In contrast, adding 4% titanium and 6% YSZ to the sample composition increases the decomposition temperature above 1000 °C. A further increase in YSZ content, up to 31%, leads to a decomposition temperature of approximately 1000 °C. These findings show that the presence of titanium and its conversion to TiO2, together with YSZ, increases the stability of the composite materials and thus reduces HAp decomposition and affects the thermal behavior of the sintered samples.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2024 Seyyed Mohsen Fatemi, Iman Mobasherpour, Leyla Nikzad, Mansour Razavi, Leyla karamzadeh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












