Effects of pH and calcination temperature on gel-combustion synthesizability of BaZr0.8Y0.2O3 perovskite
- 1 Ceramics Department, Materials and Energy Research Center (MERC), Karaj, Iran
Abstract
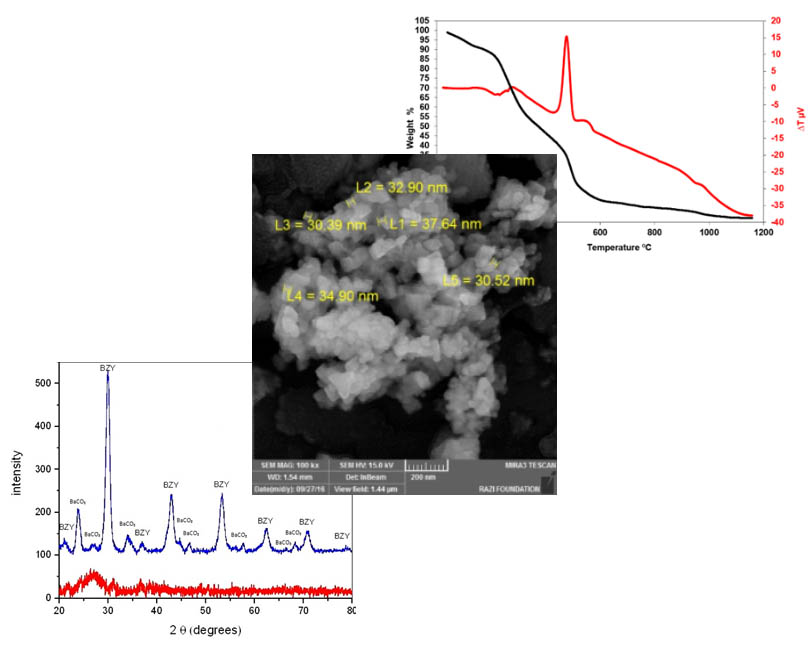
Solid oxide fuel cells with their advantages such as high efficiency are now considered as efficient power generation equipment. Because of its proton conductivity, perovskite is used in ceramic fuel cell electrolyte, and the addition of dopant can improve its proton conductivity. In this research, BaZr0.8-xSrxY0.2O3 (x=0, 0.05, 0.1, and 0.15) perovskites were synthesized by gel-combustion method. Barium nitrate, zirconium nitrate, yttrium nitrate, and strontium nitrate were used as raw materials. Based on DTA and TGA analyses, the required temperature for calcination was determined to be around 1000 °C. XRD and FTIR analyses were used to identify the phases. The synthesis was carried out under different conditions and the effects of pH and dopant percentage on the morphology and size of the particles were investigated by FESEM. The sintering process was completed at different temperatures and a relative density of 94% was obtained at 1470 °C.
Downloads
References
Copyright (c) 2023 Mohammad Reza Foroughi, Zahra Khakpour, Amir Maghsoudipour

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












