Microwave sintering of ZrB2-based ceramics: A review
- 1 Otto Schott Institute of Materials Research, Friedrich Schiller University, Jena, Germany
- 2 Volvo Trucks Technology, Eketrägatan 25, Göteborg, Sweden
- 3 Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Department, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, 247667, India
Abstract
Recently, microwave sintering has absorbed remarkable attention on the basis of enhanced microstructural/mechanical characteristics in comparison with conventional sintering techniques based on powder technology. This method not only can be employed for the processing of metals, alloys, and metal matrix composites but also for the manufacturing of advanced ceramics and ceramic matrix composites. Zirconium diboride (ZrB2) as an interesting member of ultrahigh temperature ceramics is one of the most undertaking candidates in modern structural ceramics applications. This paper reviews the processing-densification-mechanical properties correlations in microwave-sintered ZrB2-based ceramics and composites. The text concentrates on the microwave-assisted production of ZrB2 divided into two categories: synthesis of ZrB2 powders by microwave sintering and sintering of ZrB2-based ceramics and composites by microwave sintering. The effects of some additives and reinforcements, such as B4C, SiC, TiC, and MgO, on zirconium diboride's densification and mechanical properties are summarized.
Downloads
References
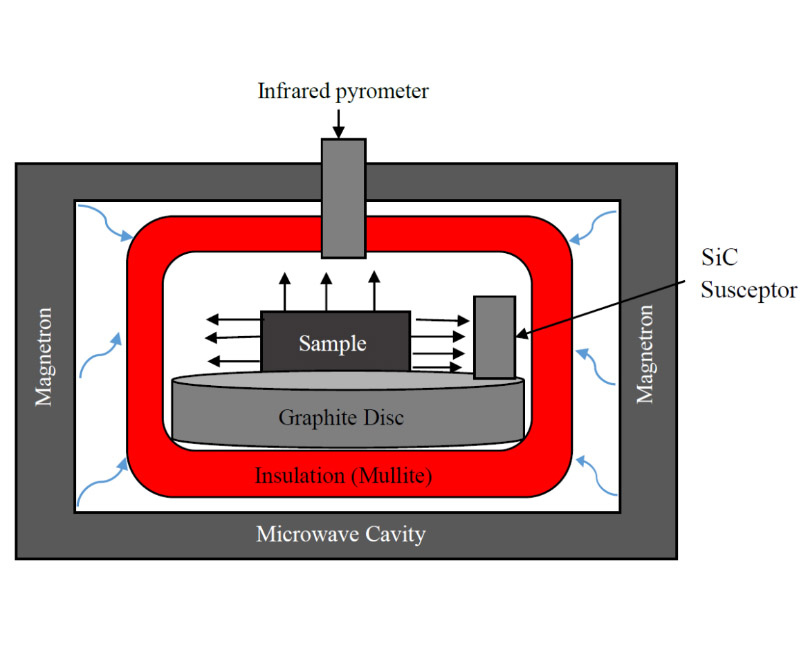
Copyright (c) 2023 Samira Savani, Mohammad Alipour, Ankur Sharma, Dagarapu Benny Karunakar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors are the copyright holders of their published papers in Synthesis and Sintering, which are simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The full details of the license are available at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
All papers published open access will be immediately and permanently free for everyone to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, link to the full-text of papers, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose without any registration obstacles or subscription fees.












